In the world of plastic, there are quite a number of varieties to choose from and many with similarities among them, which can make selecting the best product for your project confusing. Here’s an easy question-and-answer guide to familiarize yourself with the difference between popular plastics, Polypropylene (PP) and High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and help make the project material choice clear.
Is Polypropylene (PP) the same as HDPE?
No. Polypropylene (PP) aka polypropene is a thermoplastic polymer – a versatile plastic polymer which becomes soft when heated and firm/hard when cooled. It maintains its integrity even after being cooled and heated several times. When heated to its melting point it melts to liquid form. Polypropylene is made up of the monomer, propylene. PP is a commonly used material for packaging, automotive parts, textiles, and more. What differentiates PP from HDPE or High Density Polyethylene is varying density, temperature, and UV resistance. PP has a lower density than HDPE and is therefore best used for lower weight molded parts. Its melting point ranges from 266 degrees F to 340 degrees F. Both PP and HDPE provide good chemical resistance and UV resistance; however, PP requires stabilization via additives, so HDPE may be preferred in many applications where UV resistance is a primary characteristic.
How to Tell the Difference Between HDPE and PP?
The characteristics are so similar between HDPE and PP that it can be difficult to differentiate between the two. In the world of plastics each type has its own signature scent and look when subjected to the flame test. Does the plastic drip, bubble or not change in appearance? Will the flame be a specific color or omit a particular odor? In the case of HDPE and PP the nose knows the difference between them. When each material undergoes a flame or burn test each plastic tends to drip; however, it’s in the scent they emit where they part ways. HDPE smells of melted candlewax, whereas PP smells of petroleum or a dirty engine with melted candlewax undertones – perhaps due to its additional additives to make it a stable material.
HDPE and PP Plastic: What’s the Difference?
As mentioned, when it comes to HDPE and PP plastic, there are a lot of similarities – density, temperature controls, UV resistance, etc. which makes it easy to confuse the two materials when it’s time to procure materials for manufacturing or a particular project. However, deciding between HDPE and PP plastics can result in stark differences in the overall end products. For this reason, it’s important to understand what separates HDPE and PP, as well as the inherent benefits each material can bring to your business’’s next project.
We’re exploring the benefits of both materials, showcasing their specific differences to help you pick the ideal material for your business needs. Here, a breakdown:
The Benefits of HDPE Plastic
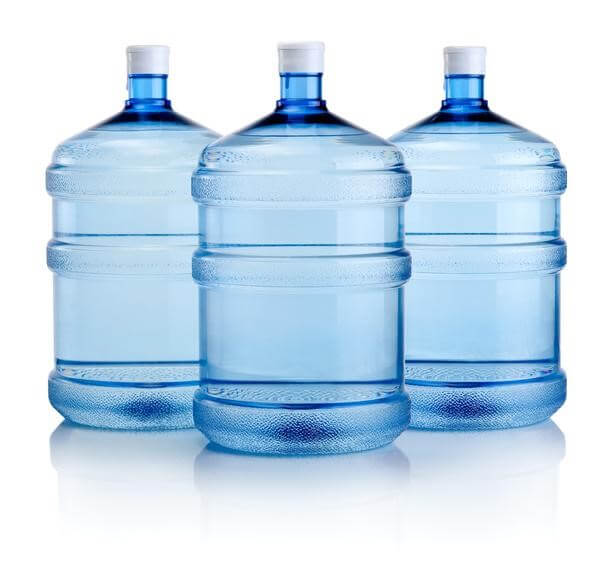

HDPE stands for high density polyethylene. HDPE is a versatile plastic known for its unique benefits. Thanks to the material’s durability and strength, HDPE is commonly used to create containers like milk and water jugs, where a 60g jug can effectively retain over a gallon of liquid without distorting its original shape.
In contrast, HDPE can also remain flexible as well. Take for example, plastic bags. Long-lasting, weather resistant, and capable of carrying weight compared to its own, HDPE is an ideal option for those looking for plastic that can withstand a variety of different stress factors while maintaining its strength—whether rigid or flexible.
HDPE is known for its resistance to mold, mildew, and corrosion, which is why it is commonly used for a variety of sanitation applications as well as for construction use. Furthermore, it can be molded into almost any shape while maintaining its lightweight, making it an ideal option when compared to other types of plastic. HDPE is more stable, dense, and hard.
[wbcr_snippet id=”703″]
The Benefits of PP Plastic

PP stands for polypropylene plastic, is a type of plastic that is specifically known for its semi-crystalline characteristic, it can be shaped and formed easily thanks to the material’s low-melt viscosity. Polypropylene is ideal for injection molding–but that is not its only use.
PP or polypropylene plastic is used in everything from fuel-injected molds, automotive parts, ropes, carpets, and clothing to name a few. It’s an affordable commercial material that offers businesses strong chemical resistance against a broad selection of bases and acids. This means that if the PP needs to be cleaned, it is likely to be resistant to chemical cleansers over longer periods of time than similar plastics–providing easier cleaning and maintenance.
Additionally, PP is a lighter material compared to other types of plastic. This makes it an ideal alternative across a variety of commercial applications, whether businesses are looking for a plastic to create reusable containers or textiles.
Is HDPE or PP the Right Material for My Business?
HDPE plastic and PP plastic both share similar benefits. In addition to being highly malleable, they are practically impact resistant, meaning strength does not have to be a concern when these plastics are in use. Additionally, both HDPE and PP are considered heat-tolerant and low in terms of toxicity to humans. This may be another factor to consider if the plastic is going to be used for items such as food and beverage containers.
Finally, both HDPE and PP plastics can be recycled, which is a benefit all, but especially for environmentally conscious businesses focused upon creating a large number of items for temporary use (e.g., food containers, signage).
Overall, there are several advantages associated with using HDPE and PP that businesses will want to look at before making a final decision. Doing so can ensure that they are making the most of their budget when it comes to investing in a specific variety of plastic.

